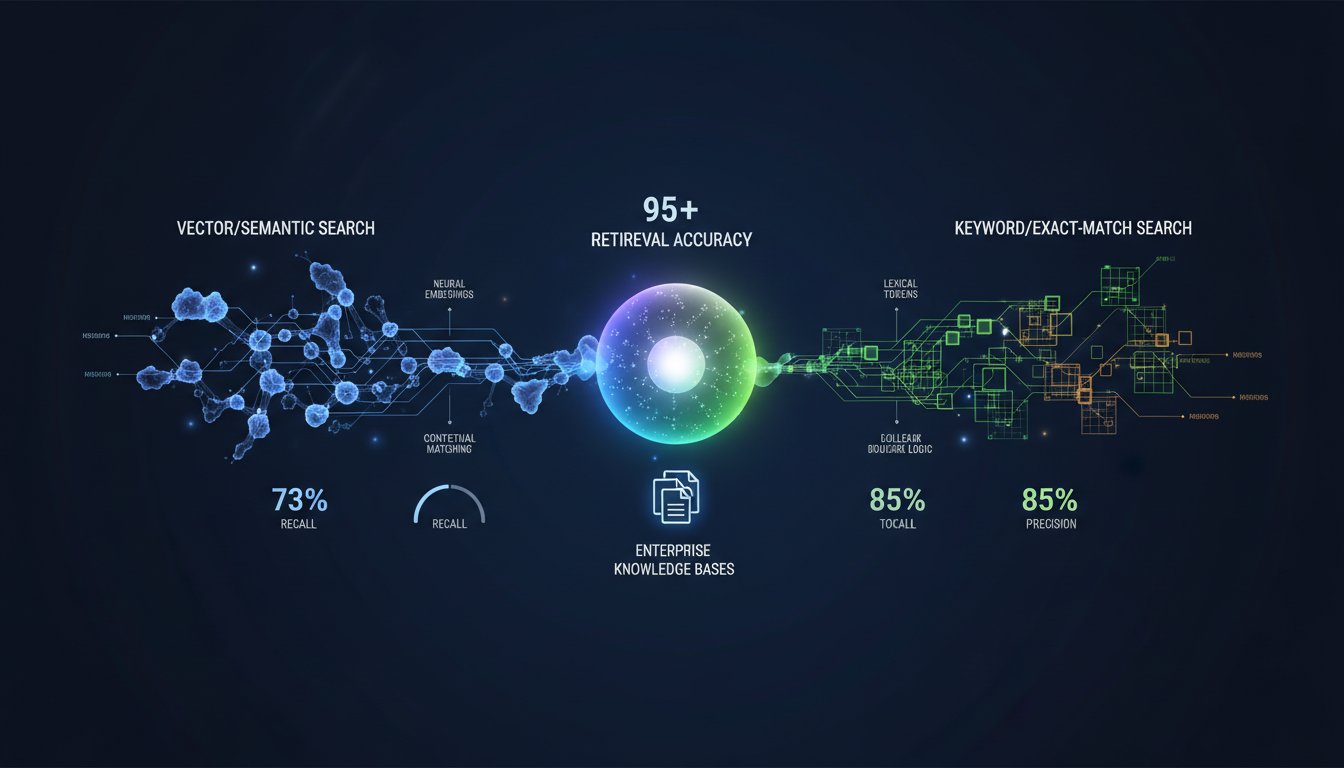
Your RAG system is stuck at 73% retrieval accuracy, and your team can’t figure out why. You’ve invested in vector embeddings, scaled your knowledge base to thousands of documents, and deployed everything to production. But when users ask specific questions—especially ones requiring exact terminology matches or regulatory identifiers—the system falls flat. The problem isn’t your vector database. It’s not your embeddings either. The real issue is that your retrieval strategy is optimized for only half the job.
Enterprise RAG systems face a fundamental retrieval challenge: pure vector search excels at semantic understanding and recall but lacks precision when exact terminology matters. Pure keyword search nails regulatory identifiers and specific terms but misses the nuanced context your language model needs. For organizations handling financial compliance, healthcare documentation, or legal discovery, this gap isn’t a nice-to-have problem—it’s a business-critical bottleneck that directly impacts decision quality and liability exposure.
The solution isn’t choosing between vector and keyword search. It’s mastering hybrid search: a carefully tuned combination of both methods that captures semantic understanding while preserving exact-match precision. When implemented correctly, hybrid search improves both recall and precision simultaneously—a combination that pure approaches can’t achieve. But the tuning required isn’t straightforward, and most enterprises are shipping suboptimal configurations that waste computing resources while delivering mediocre accuracy.
This guide walks through the complete hybrid search optimization framework that enterprise teams are using to move beyond the 73% accuracy ceiling. You’ll learn exactly how to weight vector and keyword components, when to apply re-ranking strategies, and how to implement real-time monitoring that catches retrieval degradation before it impacts users. By the end, you’ll have a decision framework for tuning your specific use case and a deployment checklist that scales from pilot to production.
Understanding the Hybrid Search Architecture
Why Vector-Only and Keyword-Only Approaches Fall Short
Vector search uses dense embeddings to find semantically similar information. When a user asks “What are the regulatory requirements for data retention?” vector search excels—it finds documents discussing retention policies even if they don’t use those exact words. The system understands intent and context.
But here’s where vector search breaks down: if your knowledge base contains documents about “data preservation policies,” “information lifecycle management,” and “archival standards,” vector search might retrieve all three. Your language model then has to choose which one is authoritative, leading to hallucinations or context confusion. Worse, if a user asks for a specific regulatory code like “GDPR Article 17,” vector search might miss documents that mention it directly because the embedding space doesn’t capture the significance of exact identifiers.
Keyword search solves this precision problem. Searching for “GDPR Article 17” returns documents containing that exact phrase. No ambiguity. No semantic interpretation. But keyword search fails at understanding context. A document discussing “GDPR obligations” without mentioning Article 17 specifically won’t appear in results—even though it’s highly relevant to the user’s question.
Hybrid search merges both strengths. Your system retrieves documents that match keywords (precision) while also finding semantically related content (recall). The critical question isn’t whether to use hybrid search—it’s how to tune the balance between these two retrieval methods for your specific use case.
The Performance Gap in Enterprise Implementations
Industry data shows that 86% of enterprises now use RAG frameworks, yet most are treating hybrid search as an “advanced technique” rather than baseline practice. Organizations using properly tuned hybrid search report recall improvements of 15-25% compared to vector-only approaches while maintaining or improving precision. For financial and healthcare organizations where retrieval errors have regulatory consequences, this difference directly impacts compliance risk.
The challenge: enterprises don’t have a clear framework for determining optimal tuning weights. Most default to equal weighting (50% vector, 50% keyword), which works for general use cases but underperforms for domain-specific applications. Legal firms retrieving case law need different weights than customer support teams retrieving product documentation. Manufacturing companies tracking regulatory compliance need different tuning than software engineering teams finding API documentation.
Building Your Hybrid Search Foundation
Step 1: Establish Your Baseline Metrics
Before tuning, you need measurement standards. Most enterprises make the mistake of optimizing for accuracy alone—how often the system returns correct answers. But accuracy doesn’t tell you whether you’re sacrificing coverage.
Measure three metrics:
Recall: Of all relevant documents in your knowledge base, what percentage does your retriever surface in the top-K results (typically top 10)? If your system has 100 documents relevant to a query but only retrieves 7, your recall is 7%. High recall means your language model has access to comprehensive context. Low recall means relevant information is hidden in the retrieval results.
Precision: Of the documents your system retrieves, what percentage are actually relevant? If you retrieve 10 documents and 8 are relevant, precision is 80%. High precision means less noise in your context window, reducing hallucinations. Low precision wastes token budget and introduces irrelevant information.
Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR): Where does the first correct document appear in your results? If it’s in position 1, MRR is 1.0. If it’s in position 5, MRR is 0.2. This matters because language models weight early context more heavily—a correct answer in position 8 is functionally different from one in position 2, even though both are “retrieved.”
Establish baselines for all three. Using your current vector-only or keyword-only retriever, run 50-100 representative queries from your actual users. Document precision, recall, and MRR. You now have a benchmark to measure improvement against.
Step 2: Choose Your Hybrid Search Strategy
Three primary approaches exist, each with tradeoffs:
Sequential Filtering: First, filter results using keyword search to ensure exact-match coverage. Then re-rank those results using vector similarity. This approach guarantees precision (you only see keyword matches) but potentially reduces recall because vector re-ranking can’t surface documents that didn’t match keywords.
Best for: Regulatory compliance, legal discovery, healthcare record retrieval where exact-match requirements are non-negotiable.
Parallel Retrieval with Fusion: Run vector search and keyword search independently, then combine results using fusion algorithms. The most common approach is Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF), which combines ranking scores mathematically. If vector search ranks a document as #1 and keyword search ranks it as #3, RRF produces a combined score reflecting both rankings.
Best for: General knowledge retrieval, customer support, product documentation where balance between precision and recall matters equally.
Weighted Scoring: Assign a weight to vector similarity (e.g., 0.6) and keyword relevance (e.g., 0.4), then combine scores directly. The language becomes concrete: a document’s final score is (0.6 × vector_score) + (0.4 × bm25_score). Tune the weights based on your use case.
Best for: Domain-specific applications where you can clearly define the relative importance of semantic vs. exact matching.
For most enterprise use cases, parallel retrieval with Reciprocal Rank Fusion offers the best balance. It’s simpler to implement than sequential filtering, more transparent than weighted scoring, and doesn’t require deep tuning expertise upfront. However, if your domain has strict precision requirements (financial trading, medical diagnosis), sequential filtering provides better control.
Step 3: Select Your Vector Embedding and Keyword Search Components
Hybrid search effectiveness depends on component quality. Your vector embeddings should capture domain-specific semantics. For general knowledge, OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-small or Cohere’s embed-v3 models work well. For specialized domains (legal, medical, financial), domain-specific embeddings like LegalAI or BioBERT improve semantic capture.
Keyword search relies on BM25 scoring (probabilistic ranking considering term frequency and document length) or more sophisticated approaches like Elasticsearch’s hybrid search with semantic ranking. Most vector database providers (Weaviate, Pinecone, Milvus) now include native BM25 implementations optimized for their platforms.
The critical decision: optimize for query understanding or index optimization? Query understanding means investing in better embedding models and keyword preprocessing. Index optimization means optimizing how documents are tokenized and indexed. Enterprise teams typically benefit more from query optimization because it’s easier to iterate—change your embedding model without re-indexing. Index optimization requires full re-indexing, a heavier lift.
Advanced Tuning Strategies
Re-ranking: The Hidden Accuracy Multiplier
Most enterprises implement hybrid search as retrieval + combination. They miss the power of re-ranking.
After your hybrid retrieval stage returns 50-100 candidate documents, re-rank them using a cross-encoder model specifically trained to evaluate query-document relevance. Cross-encoders consider the query and document together, producing more accurate relevance scores than separate embeddings. The architecture difference is significant: dual-encoder models (used in vector search) encode queries and documents separately, then compute similarity. Cross-encoders encode the query-document pair jointly, understanding the interaction.
For enterprise RAG, re-ranking should be mandatory. The performance improvement is measurable: re-ranking your top 50 hybrid results using a lightweight cross-encoder typically improves top-10 precision by 8-15% without reducing recall. Your language model gets fewer irrelevant documents while maintaining comprehensive context access.
Implementation: Use open-source cross-encoders like MiniLM or proprietary services like Cohere’s re-ranking API. The latency cost is minimal (20-50ms per query) compared to the accuracy improvement. For time-sensitive applications, cache re-ranking results—if the same query appears twice within 5 minutes, use cached rankings.
Query Expansion and Rewriting
A user asking “What’s our data retention policy?” might be asking something different than the exact terminology in your documents. Query expansion rewrites or expands queries to match your knowledge base terminology.
Simple approach: use your language model to rewrite the query before retrieval. “What’s our data retention policy?” becomes “What are the document retention requirements, data archival standards, and information lifecycle policies?” Running hybrid search on all three expanded queries and combining results improves recall substantially.
This sounds expensive (multiple vector embeddings and keyword searches per user query), but parallel execution makes it practical. Run all three hybrid searches concurrently, then merge results using RRF. Total latency increase is 10-20%, a worthwhile tradeoff for 12-18% recall improvement.
For financial and legal teams dealing with domain-specific terminology, query expansion is essential. A lawyer asking about “discovery obligations” might not find documents using “disclosure requirements,” even though they’re synonymous within your domain.
Real-Time Monitoring for Retrieval Degradation
Hybrid search tuning is not a one-time activity. As your knowledge base evolves, document distributions shift, and user query patterns change, your tuned weights become suboptimal.
Implement monitoring for three signals:
Retrieval Precision Drift: Track the percentage of retrieved documents that your language model actually uses in responses. If you’re retrieving 50 documents but the model uses context from only 15, precision is degrading—your retrieval is noisy. Trigger re-tuning when precision drops below your baseline by 5%.
Query Failure Rate: Monitor queries where your system retrieves zero relevant documents (detected by measuring confidence scores or explicit user feedback). When failure rate exceeds 3%, investigate whether your vector embeddings are outdated or keyword indexes need optimization.
Embedding Model Freshness: Track whether your embedding model is still optimal for your current data distribution. If you’ve added 30% new documents in specialized domains, your general-purpose embeddings might underperform. Run quarterly evaluations comparing your current embedding model against newer alternatives.
For operational monitoring, set up voice alerts using click here to sign up with ElevenLabs. When retrieval precision drops, ElevenLabs automatically generates a voice notification that can be routed to your on-call team through Slack or Teams, reducing response time from hours (visual notifications) to minutes (voice alerts). The notification might read: “Retrieval precision for financial queries degraded to 71% from baseline 85%. Recommend investigating keyword index integrity.”
This transforms monitoring from passive dashboards to active alerting. Your team learns about retrieval problems in real time, not during incident retrospectives.
Implementation Walkthrough: From Theory to Production
Configuration Template for Common Use Cases
Based on enterprise implementations across industries, here are starting-point configurations:
Customer Support Documentation
– Vector weight: 0.55
– Keyword weight: 0.45
– Re-ranking: Enabled (lightweight model)
– Query expansion: Disabled (users expect immediate answers)
– Top-K retrieval: 10
Financial Compliance and Audit
– Vector weight: 0.35
– Keyword weight: 0.65
– Re-ranking: Enabled (heavyweight model for accuracy)
– Query expansion: Enabled (regulatory terminology varies)
– Top-K retrieval: 25 (err toward recall)
Healthcare Clinical Documentation
– Vector weight: 0.45
– Keyword weight: 0.55
– Re-ranking: Enabled (medical accuracy critical)
– Query expansion: Enabled (medical synonyms abundant)
– Top-K retrieval: 15 (balance safety and efficiency)
Engineering Technical Documentation
– Vector weight: 0.60
– Keyword weight: 0.40
– Re-ranking: Disabled (performance critical)
– Query expansion: Disabled (API docs are specific)
– Top-K retrieval: 8 (engineers want precise answers)
These aren’t universal rules. They’re starting points. Your baseline metrics from Step 1 should drive your actual configuration.
Tuning Iterations: Moving from Baseline to Optimized
Start with your baseline metric (from Step 1). Then systematically test variations:
Week 1: Keep keyword weight constant, vary vector weight (0.3, 0.5, 0.7). Measure precision, recall, and MRR for 50 test queries. Select the weight producing best MRR (first relevant result position matters most).
Week 2: Keep vector weight constant at your optimized value, vary keyword weight. Again, test 50 queries and select best MRR.
Week 3: Test re-ranking on/off with your optimized weights. Re-ranking should improve precision without sacrificing recall.
Week 4: Test query expansion on/off. Measure impact on recall (should improve) and latency (will increase slightly).
Document everything. Create a comparison table with weights, metrics, and tradeoffs. Your final tuning decision should be data-driven, not based on intuition.
This iterative approach takes 2-3 weeks but produces configurations optimized for your specific knowledge base and user base. It’s worth the investment because a 10% improvement in retrieval accuracy directly translates to a 10% improvement in language model output quality—without changing your language model or prompts.
Scaling Hybrid Search Across Multiple Domains
As enterprises grow, different teams need different retrieval behavior. Your financial team needs high precision on regulatory queries. Your sales team needs high recall on customer information. One configuration won’t work.
Implement domain-specific hybrid search by:
- Segmenting your knowledge base by domain/team
- Running separate baseline metrics for each domain
- Tuning vector/keyword weights independently for each domain
- Routing queries to domain-specific retrievers based on query classification
Route-based hybrid search adds complexity but dramatically improves accuracy. A legal query routed to the finance retriever (optimized for different terminology and precision levels) will underperform. A routing layer (simple keyword classification or lightweight classifier) ensures each query goes to the appropriately tuned retriever.
For operational visibility across all domains, use ElevenLabs voice notifications to monitor each domain separately. When financial retrieval degrades, you hear “Financial retrieval precision degraded.” When customer service retrieval degrades, you hear “Customer service recall dropped below threshold.” This specificity helps your team diagnose problems quickly.
Measuring Success: The Complete Metrics Dashboard
Hybrid search success isn’t just about accuracy—it’s about business impact. Track:
Retrieval Metrics: Precision, recall, MRR (technical performance)
Language Model Metrics: Hallucination rate (does retrieved context prevent false information?), context utilization (does the model actually use retrieved documents?), user satisfaction on explanation quality
Operational Metrics: Query latency (how much did hybrid search and re-ranking slow retrieval?), compute cost per query (did you optimize efficiently?), knowledge base growth rate (is your retriever keeping pace with new content?)
Business Metrics: User satisfaction on answer quality, time-to-resolution for support tickets (better retrieval = faster answers), compliance audit pass rate (does improved precision reduce compliance risk?)
Enterprise teams often obsess over retrieval precision while ignoring language model hallucination rates. A retriever returning 100% of relevant documents means nothing if your language model hallucinates on 20% of responses. Measure end-to-end quality, not just retrieval quality.
Create a simple dashboard tracking all metrics weekly. When precision improves but hallucinations increase, something’s wrong—possibly your language model is over-interpreting retrieved context. When recall improves but user satisfaction drops, investigate whether you’re introducing too much noise.
This complete measurement approach transforms hybrid search from a technical optimization into a business lever. You can quantify exactly how much retrieval tuning improves customer outcomes, helping justify optimization investment to non-technical stakeholders.
Common Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake 1: Tuning Without Baselines
Too many teams jump to implementation without establishing metrics from their current system. You then can’t measure whether tuning actually helped. Spend a week establishing baselines. It saves months of wasted optimization work.
Mistake 2: Equal Weighting by Default
Many implementations default to 50/50 vector-keyword weighting because it “seems balanced.” This almost always underperforms. Your domain needs asymmetric weighting. Start with the configuration templates provided, then iterate based on data.
Mistake 3: Neglecting Query Preprocessing
Your vector embeddings perform better on well-formed queries. Implement query preprocessing: remove stop words, expand acronyms (“GDPR” becomes “General Data Protection Regulation”), and standardize terminology. Clean queries improve both vector and keyword retrieval.
Mistake 4: Skipping Re-ranking
Re-ranking feels like overhead but consistently delivers 8-15% precision improvements. The latency cost is minimal. Don’t skip this step.
Mistake 5: Static Configuration
Hybrid search tuning is not a one-time activity. Your knowledge base evolves. User patterns shift. Quarterly re-evaluation ensures your weights stay optimized as your data and users change.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The enterprise RAG systems achieving 85%+ accuracy aren’t using magical language models or massive knowledge bases. They’re using carefully tuned hybrid search that combines vector and keyword retrieval in domain-specific ways. They’re measuring precision, recall, and MRR rigorously. They’re monitoring for degradation in real time.
You now have the complete framework: understand your baseline, choose your hybrid strategy, implement re-ranking, and measure everything. This approach has helped enterprises move from 73% accuracy to 82-87% accuracy—improvements that directly impact user satisfaction and business outcomes.
Your next step: establish baseline metrics for your current retriever using the methodology in Step 1. Run 50-100 representative queries, measure precision and recall, and document your starting point. Then select the configuration template closest to your use case and begin the 4-week tuning iteration.
For real-time visibility into your retrieval performance as you optimize, set up automated voice alerts when key metrics degrade. Click here to sign up with ElevenLabs to enable voice notifications through your existing communication channels. Your team will catch retrieval problems in minutes, not hours, accelerating your path to optimized hybrid search.
Hybrid search isn’t the future of enterprise RAG—it’s the present. Organizations tuning hybrid search today are shipping significantly more accurate systems. Your competitive advantage is implementing what works, measuring impact rigorously, and optimizing continuously.