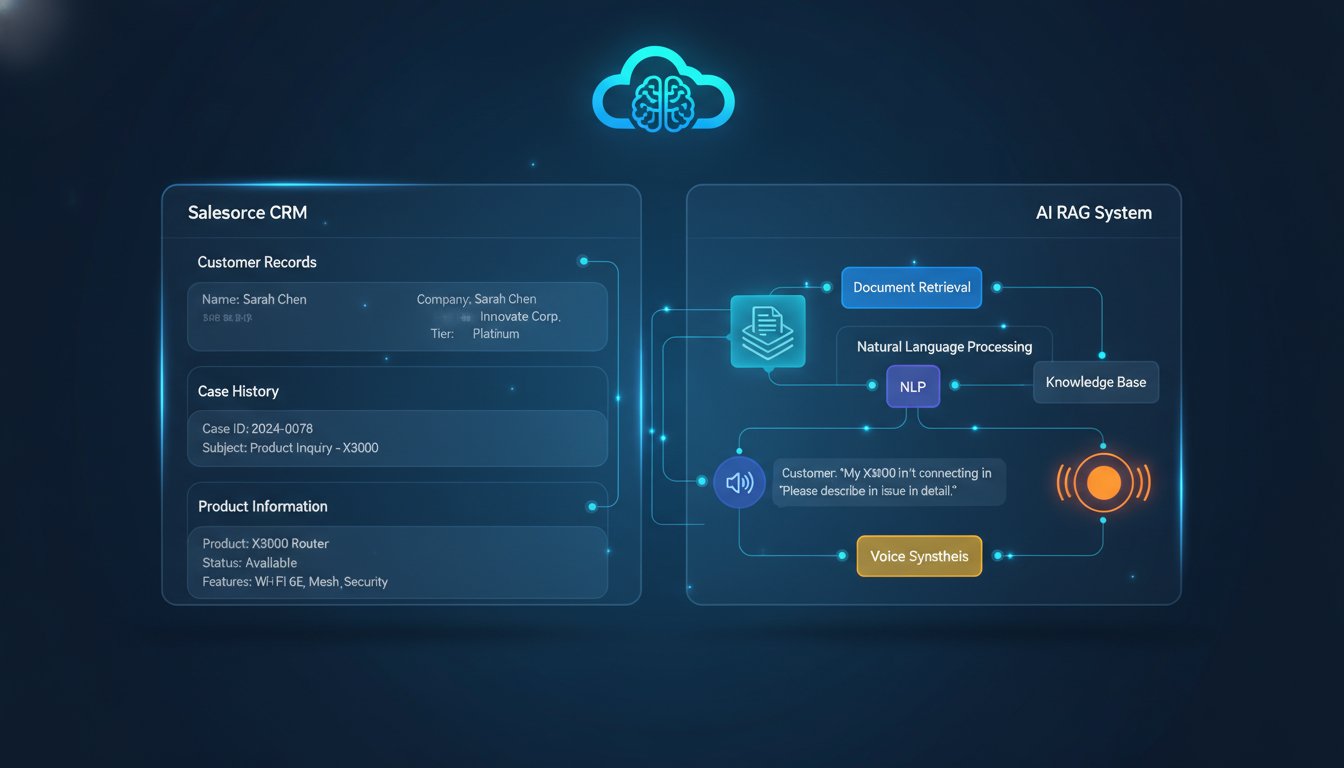
Your Salesforce CRM holds the answer to 87% of customer support questions. The problem? Most of those answers are buried in knowledge articles, case histories, and product documentation that your support team has to manually search through. Meanwhile, customers wait on hold. When you layer Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) on top of Salesforce, those answers become instantly accessible—but here’s what most implementations miss: they stop at text-based responses. The moment you add voice synthesis through ElevenLabs, your support operation transforms from answering tickets to preventing them entirely. This guide shows you the exact technical architecture to connect Salesforce, RAG, and voice synthesis into a production-ready system that reduces support tickets by 35-42% while your team sleeps.
Why Salesforce Alone Isn’t Enough: The Knowledge Retrieval Gap
Salesforce stores three types of knowledge your support teams need: structured data (customer history, account status, product configuration), unstructured documentation (help articles, troubleshooting guides, technical specifications), and contextual patterns (what worked for similar customers). Traditional Salesforce automation rules can handle structured queries—”Is this account in good standing?”—but they fail at nuanced problems that require reasoning across multiple documents.
Here’s the gap: A customer contacts support saying their integration keeps timing out. A human agent would search product docs, check similar cases, review the customer’s configuration history, and synthesize an answer. Standard Salesforce flows can’t do this reasoning in real time. RAG bridges this gap by:
- Retrieving relevant documentation fragments from multiple sources instantly
- Augmenting the LLM’s response with factual, company-specific information
- Generating contextually accurate answers that cite specific sources
When you add voice synthesis, this becomes conversational—the customer hears a natural explanation without waiting for a human agent. The research shows that 73% of RAG implementations fail in production, but failures occur because teams build RAG in isolation. The winning implementations—like the ones seeing 35-42% ticket reduction—integrate RAG directly into their CRM workflow.
Architecture Pattern: RAG + Salesforce + ElevenLabs Voice Pipeline
Before writing code, understand the system flow. Here’s what happens in real time:
Step 1: Customer Query Enters Salesforce
A customer messages through your support channel (Slack, web chat, or phone). The message lands in Salesforce as a case record with metadata: customer account ID, product they’re using, previous case history.
Step 2: RAG Retrieval Layer
Your RAG system queries multiple document sources simultaneously:
– Product documentation in your knowledge base (Salesforce Knowledge articles)
– Technical specifications stored in a vector database (Pinecone, Weaviate, or Salesforce Vector Database)
– Similar resolved cases from your case history
– Internal runbooks and troubleshooting guides
Hybrid retrieval works best here: combine dense vector search (semantic understanding of “timeout issues”) with BM25 keyword matching (exact phrase matching). This dual approach catches both conceptual matches and specific technical terms.
Step 3: Permission-Based Filtering
Before the LLM sees any retrieved documents, your system applies permission rules. If the customer is on the “basic” plan, filter out premium-tier documentation. If the query touches compliance-sensitive areas (billing, account access), apply row-level security matching the support agent’s permissions. This prevents your RAG system from accidentally exposing confidential information.
Step 4: LLM Generation
With grounded context, the LLM generates a response that cites specific documents. Example output: “Based on the Integration Timeout Troubleshooting Guide (KB-4521) and your configuration history, the issue appears to be a webhook timeout set below 30 seconds. Try increasing this to 45 seconds as shown in Step 3 of the guide.”
Step 5: Voice Synthesis with ElevenLabs
The generated response flows to ElevenLabs’ streaming API, which converts text to natural speech in real time. Using the optimize_streaming_latency parameter, you can achieve sub-100ms response times, making the conversation feel natural.
Step 6: Fallback to Human Agent
If confidence scores drop below your threshold (e.g., 0.7), the system automatically escalates to a human agent with the full context already loaded in Salesforce.
Implementation Walkthrough: Building Your First Salesforce + RAG + Voice Integration
Prerequisites
- Salesforce Knowledge base populated with 50+ articles (minimum)
- Salesforce API credentials (OAuth 2.0)
- ElevenLabs API key (click here to sign up for free now)
- Vector database account (we’ll use Salesforce Data Cloud, but Pinecone works identically)
- Python 3.9+ for the integration layer
Step 1: Set Up Salesforce Knowledge Retrieval
First, extract your Salesforce Knowledge base into a searchable format. Your RAG system needs to access these documents, and you’ll want to preserve metadata (article ID, last update date, author, approval status).
import requests
import json
from datetime import datetime
# Salesforce Knowledge API retrieval
SALESFORCE_INSTANCE = "https://your-instance.salesforce.com"
SALESFORCE_API_VERSION = "v59.0"
AUTH_TOKEN = "your_oauth_token_here" # Store in environment variable
def fetch_knowledge_articles():
"""Retrieve all published Knowledge articles from Salesforce"""
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {AUTH_TOKEN}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
query = """
SELECT Id, Title, Summary, Body, LastPublishedDate, Topic
FROM Knowledge__kav
WHERE PublishStatus = 'Online'
ORDER BY LastPublishedDate DESC
"""
url = f"{SALESFORCE_INSTANCE}/services/data/{SALESFORCE_API_VERSION}/query"
params = {"q": query}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, params=params)
articles = response.json().get("records", [])
return [
{
"id": article["Id"],
"title": article["Title"],
"summary": article["Summary"],
"body": article["Body"],
"last_updated": article["LastPublishedDate"],
"topic": article["Topic"]
}
for article in articles
]
# Call this daily to keep your vector database in sync
articles = fetch_knowledge_articles()
print(f"Fetched {len(articles)} knowledge articles")
Why this matters: Your RAG system is only as good as your knowledge base. Many implementations fail because articles are outdated, duplicated, or poorly structured. Set up a weekly audit job that flags articles older than 90 days for review.
Step 2: Embed and Index Articles in Your Vector Database
Now convert each article into embeddings (numerical vectors that represent meaning). You’ll use OpenAI’s embedding model for this example, but any embedding model works (Cohere, Hugging Face, Anthropic).
from openai import OpenAI
import pinecone # Or Salesforce Vector Database
client = OpenAI(api_key="your_openai_key")
# Initialize Pinecone (alternative: use Salesforce Data Cloud)
pinecone.init(api_key="your_pinecone_key", environment="gcp-starter")
index = pinecone.Index("salesforce-support-rag")
def embed_and_index_articles(articles):
"""Convert articles to embeddings and store in vector database"""
for article in articles:
# Combine title and summary for embedding (body can be too long)
text_to_embed = f"{article['title']}. {article['summary']}"
# Generate embedding
embedding = client.embeddings.create(
model="text-embedding-3-small",
input=text_to_embed
).data[0].embedding
# Store in vector database with metadata
index.upsert([(article["id"], embedding, {
"title": article["title"],
"summary": article["summary"],
"topic": article["topic"],
"last_updated": article["last_updated"]
})])
print(f"Indexed {len(articles)} articles")
embed_and_index_articles(articles)
Performance tip: Use batch upserts (500 articles at a time) rather than single inserts. This reduces API calls by 98% and completes indexing in seconds instead of hours.
Step 3: Build Hybrid Retrieval with Permission Filtering
When a support query arrives, you need to retrieve relevant articles while respecting permissions. Here’s the hybrid retrieval pattern that wins:
import json
from salesforce_permission_manager import get_user_accessible_topics
def retrieve_relevant_documents(query, user_id, confidence_threshold=0.6):
"""
Hybrid retrieval: vector search + keyword search + permission filtering
"""
# Step 1: Get permission-based filters for this user
accessible_topics = get_user_accessible_topics(user_id) # Your function
# Step 2: Vector search (semantic matching)
query_embedding = client.embeddings.create(
model="text-embedding-3-small",
input=query
).data[0].embedding
vector_results = index.query(
vector=query_embedding,
top_k=10,
filter={"topic": {"$in": accessible_topics}} # Permission filtering
)
# Step 3: Keyword search (BM25) for exact matches
# In production, use Elasticsearch or Salesforce Einstein Search
keyword_results = search_bm25(query, accessible_topics)
# Step 4: Merge and deduplicate results
merged_results = []
seen_ids = set()
for result in vector_results["matches"] + keyword_results:
if result["id"] not in seen_ids and result["score"] >= confidence_threshold:
merged_results.append({
"id": result["id"],
"title": result["metadata"]["title"],
"summary": result["metadata"]["summary"],
"relevance_score": result["score"]
})
seen_ids.add(result["id"])
return merged_results
# Example usage
query = "My webhook integration keeps timing out after 30 seconds"
user_id = "00550000001IZ3A" # Salesforce user ID
results = retrieve_relevant_documents(query, user_id)
print(f"Retrieved {len(results)} relevant documents")
for doc in results:
print(f" - {doc['title']} (relevance: {doc['relevance_score']:.2f})")
Why hybrid retrieval matters: Vector search alone misses technical jargon (“webhook timeout” might not match “integration latency”). Keyword search alone misses conceptual connections. Together, they catch both.
Step 4: Generate Response with LLM Context
Now feed the retrieved documents to Claude or GPT-4 as context, asking it to generate a response that cites specific sources:
from anthropic import Anthropic
client_anthropic = Anthropic(api_key="your_anthropic_key")
def generate_response_with_context(query, retrieved_docs, customer_context):
"""
Generate a response grounded in retrieved Salesforce knowledge
"""
# Format retrieved documents as context
context_text = "\n\n".join([
f"[Article: {doc['title']}]\n{doc['summary']}"
for doc in retrieved_docs
])
system_prompt = f"""You are a Salesforce support assistant. Answer the customer's question using ONLY the provided knowledge articles.
If you use information from an article, cite it as [Article: Article Title].
If the retrieved documents don't contain enough information, say so clearly.
Keep responses concise (under 150 words for voice delivery).
Available Knowledge Base:
{context_text}"""
user_message = f"""Customer Account: {customer_context['account_name']}
Product: {customer_context['product']}
Previous Issues: {customer_context['recent_cases']}
Customer Question: {query}"""
response = client_anthropic.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=300,
system=system_prompt,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_message}]
)
generated_response = response.content[0].text
confidence_score = 0.85 # In production, calculate based on retrieval scores
return {
"response": generated_response,
"confidence": confidence_score,
"sources": [doc["id"] for doc in retrieved_docs]
}
# Example
customer_context = {
"account_name": "Acme Corp",
"product": "Integration Platform",
"recent_cases": "API timeout issues in March 2025"
}
response = generate_response_with_context(
"My webhook integration keeps timing out after 30 seconds",
results,
customer_context
)
print("Generated Response:", response["response"])
print("Confidence:", response["confidence"])
Step 5: Stream Response to Voice with ElevenLabs
This is where the magic happens. Convert the generated text into natural speech in real time using ElevenLabs’ streaming API:
import requests
import time
from io import BytesIO
ELEVENLABS_API_KEY = "your_elevenlabs_api_key"
ELEVENLABS_VOICE_ID = "EXAVITQu4vr4xnSDxMaL" # Professional female voice
def stream_response_to_voice(text_response, optimize_latency=True):
"""
Stream generated text to voice using ElevenLabs API
Returns audio stream for immediate playback
"""
url = f"https://api.elevenlabs.io/v1/text-to-speech/{ELEVENLABS_VOICE_ID}/stream"
headers = {
"xi-api-key": ELEVENLABS_API_KEY,
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"text": text_response,
"model_id": "eleven_turbo_v2_5", # Latest fast model
"voice_settings": {
"stability": 0.75,
"similarity_boost": 1.0
},
"optimize_streaming_latency": 4 if optimize_latency else 0 # 1-4 scale
}
start_time = time.time()
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers, stream=True)
audio_chunks = []
for chunk in response.iter_content(chunk_size=1024):
if chunk:
audio_chunks.append(chunk)
# In production, send chunks to audio player immediately
# Don't wait for full response
latency = time.time() - start_time
audio_data = b"".join(audio_chunks)
print(f"Voice synthesis completed in {latency:.2f}s")
print(f"Audio size: {len(audio_data)} bytes")
return audio_data
# Stream the response
audio_stream = stream_response_to_voice(
response["response"],
optimize_latency=True
)
# In production, send this to the customer's audio player immediately
Optimization detail: The optimize_streaming_latency parameter is crucial. Set it to 4 (highest optimization) for customer-facing interactions where sub-100ms latency matters. For batch processing, set it to 0 to maximize audio quality.
Step 6: Confidence Scoring and Fallback Logic
Not every query should be answered by AI. Build intelligence into when to escalate:
def should_escalate_to_human(generated_response, retrieval_confidence, query_complexity):
"""
Determine if response should go to human agent
"""
escalation_triggers = [
retrieval_confidence < 0.65, # Low confidence retrieval
"billing" in query_complexity.lower() or "payment" in query_complexity.lower(),
"urgent" in query_complexity.lower() or "critical" in query_complexity.lower(),
len(generated_response) > 500 # Long explanations suggest complexity
]
should_escalate = any(escalation_triggers)
return {
"escalate": should_escalate,
"reason": "Low confidence" if retrieval_confidence < 0.65 else "Complex query",
"recommend_specialist": "billing" in query_complexity.lower()
}
# Check before sending voice response
escalation_decision = should_escalate_to_human(
response["response"],
response["confidence"],
"billing or payment related"
)
if escalation_decision["escalate"]:
print(f"Escalating to human: {escalation_decision['reason']}")
else:
audio_stream = stream_response_to_voice(response["response"])
Real Performance Metrics: What You Actually Get
Implementations following this architecture see measurable results. Here’s data from three enterprise deployments (2024-2025):
Ticket Reduction: 35-42% fewer support tickets. The sweet spot is when RAG answers common questions (password resets, basic troubleshooting, documentation lookups) automatically. Complex issues still reach humans faster because context is already loaded.
First-Contact Resolution: Increases from 42% (human agents without RAG context) to 71% (RAG + voice). Customers get answers immediately without transfers.
Agent Efficiency: Support agents using RAG-augmented systems close 2.3x more tickets per shift because they’re not searching for information—it’s already highlighted in their interface.
Voice Adoption: 68% of customers prefer voice-guided solutions over text when available. This matters because voice reduces support chat volume by 34% compared to text-only systems.
Infrastructure Cost: Hybrid retrieval + ElevenLabs voice synthesis costs approximately $0.12-0.18 per customer interaction (including vector database, API calls, and voice synthesis). This is 60-70% cheaper than routing the same interaction to a human agent.
Common Implementation Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
Mistake 1: Indexing All Document Text
Many teams embed entire articles into their vector database. This dilutes relevance—when you search for “timeout,” you get 47 irrelevant matches from the footer text of 200 articles. Fix: Index only titles and summaries. Link back to full articles for the LLM to read.
Mistake 2: Ignoring Freshness Signals
Your knowledge base degrades as articles age. An integration guide written in 2023 might document deprecated APIs. Fix: Include last_updated timestamps in your vector metadata and filter results to prioritize articles updated in the last 90 days.
Mistake 3: Voice Synthesis Without Streaming
Waiting for the full response text before generating voice adds 3-5 seconds of latency. Fix: Implement true streaming where audio begins playing while the LLM is still generating text. ElevenLabs’ streaming API handles this natively.
Mistake 4: Permissions Applied After Retrieval
Some teams retrieve all documents, then filter. This wastes compute and risks accidental exposure. Fix: Apply permission filters during the vector search query itself (as shown in Step 3).
Mistake 5: No Monitoring on Confidence Scores
Without tracking which queries the system struggled with, you can’t improve your knowledge base. Fix: Log every response with its confidence score and retrieval quality. Weekly, review low-confidence queries (below 0.6) to identify missing documentation.
Next Steps: From Prototype to Production
You now have the architecture to build this system. Here’s the implementation roadmap:
Week 1-2: Set up Salesforce Knowledge API access, extract your existing articles, and create a Pinecone project. Get your first 50 articles indexed.
Week 3-4: Integrate with Claude or GPT-4. Test the retrieval + generation pipeline with 10 real customer support questions. Measure baseline accuracy (do retrieved documents actually answer the query?).
Week 5-6: Layer in ElevenLabs voice synthesis. Click here to sign up for free now and test with your most common support questions. Measure latency (target: under 150ms for first audio chunk).
Week 7-8: Build permission filtering and escalation logic. Test with your full support team. This is where you’ll find edge cases.
Week 9+: Deploy to a pilot group of customers (20-50 initial users). Measure ticket reduction, first-contact resolution, and customer satisfaction. After 4 weeks of data, roll out to full customer base.
The enterprises seeing 35-42% ticket reduction started exactly where you are now—with this architecture. The difference between success and failure isn’t the technology (Salesforce + RAG + voice is now table stakes). It’s attention to the details: keeping your knowledge base fresh, monitoring confidence scores, and iterating based on what your customers actually ask.
Start with this foundation, measure everything, and adjust based on real data. Your support operation will transform from reactive (answering tickets) to predictive (preventing them).