Your enterprise RAG system works fine with text. Retrieval is fast, costs are predictable, and your knowledge base flows smoothly into LLM responses. Then someone asks: “Why can’t we make this conversational with voice? Why can’t we auto-generate training videos from our retrieved content?”
Suddenly, you’re facing a new set of constraints. Voice synthesis adds latency. Video generation multiplies costs. And the architectural patterns that worked for text retrieval break down when you need to orchestrate parallel pipelines for audio output and video creation simultaneously.
This is the multimodal RAG integration challenge—and most enterprise teams hit it unprepared. The problem isn’t that voice and video integrations are impossible; it’s that naive implementations create cascading failures: retrieval delays compound with synthesis delays, context windows fragment across modalities, and cost per query balloons from cents to dollars.
In this guide, we’ll walk through how to architect production-grade multimodal RAG systems that combine real-time voice synthesis and automated video generation without sacrificing performance, cost efficiency, or retrieval accuracy. We’ll examine the actual trade-offs, show you where teams stumble, and provide the architectural patterns that leading enterprises are using in 2026 to solve this problem.
The Multimodal RAG Latency Paradox
Your baseline RAG system operates on a simple timeline:
- Query ingestion (5–10ms)
- Vector embedding (50–100ms)
- Retrieval from vector DB (20–50ms)
- LLM context window creation (10–20ms)
- Token generation (variable, typically 100–500ms for full response)
- Total: 200–700ms
Users accept this. It feels interactive.
Now introduce voice synthesis. After your LLM generates the final response, you need to:
- Send text to ElevenLabs API (5–10ms network latency)
- Wait for audio generation (500–2000ms depending on text length and voice model complexity)
- Stream audio back to client (network dependent)
- Additional latency: 600–2500ms
Your “interactive” experience just became a 1–3 second wait. Acceptable for voice agents, but problematic if users expect conversational responsiveness.
Add video generation on top (HeyGen pipeline for training content or demo videos), and the problem multiplies:
- Video generation from retrieved content: 3–10 seconds for short-form video
- Multi-scene composition: 10–30 seconds
- Encoding and delivery: 5–15 seconds
- Total video pipeline: 20–60 seconds
This isn’t real-time interaction—it’s batch processing masquerading as integration.
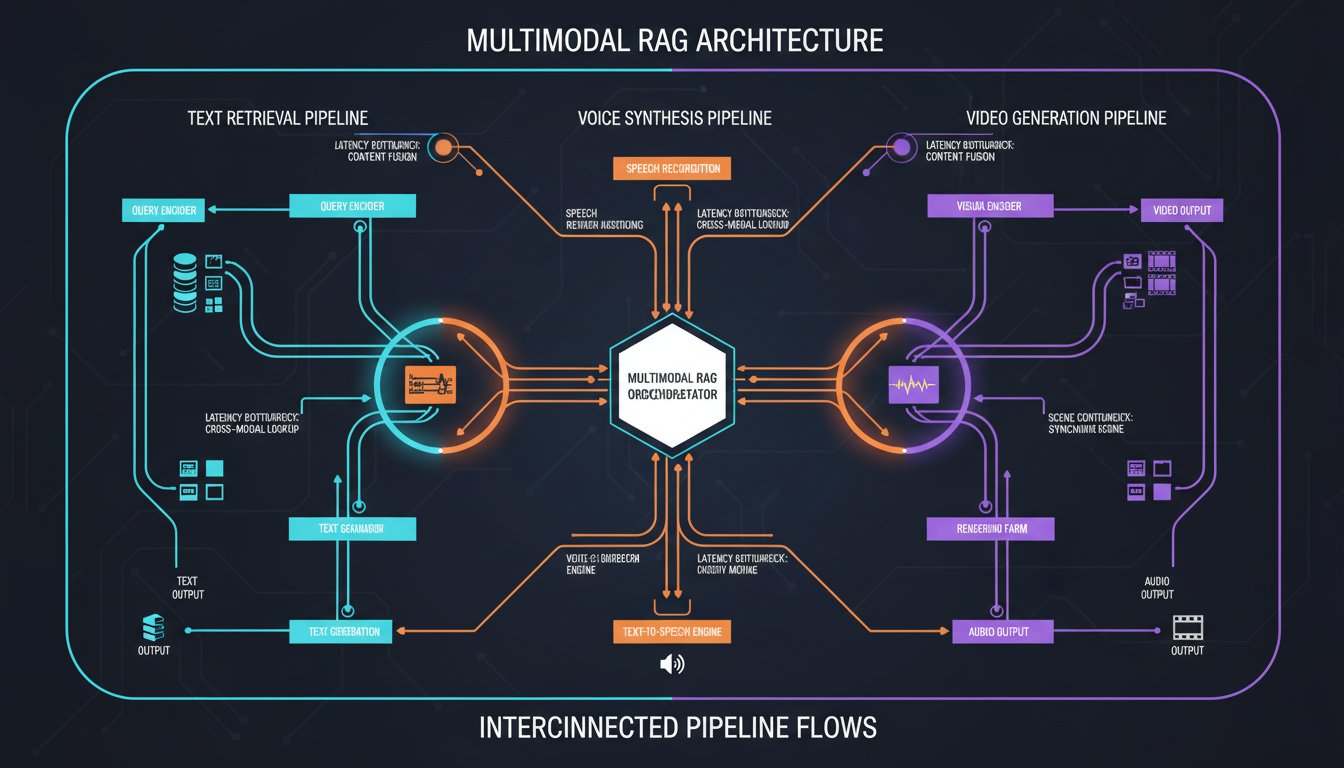
The critical insight: multimodal RAG isn’t about adding voice and video to your existing RAG pipeline. It’s about architectural bifurcation—separating real-time retrieval and synthesis paths from batch-oriented media generation paths.
Architecture Pattern 1: The Parallel Pipeline Model
Enterprise teams using this pattern split multimodal RAG into two concurrent streams:
Stream A (Real-Time Response):
1. Query → Retrieval (hybrid search, vector + keyword)
2. LLM generation (with retrieved context)
3. Text response to user (immediate)
4. Trigger async voice synthesis → ElevenLabs API (non-blocking)
5. Cache synthesized audio for reuse
Stream B (Deferred Media Generation):
1. Monitor response completion
2. Queue video generation task (HeyGen)
3. Generate training/demo video from retrieved content
4. Store in content library with metadata
5. Link to original query for future reference
Why this works:
– Users get immediate text response (same as traditional RAG)
– Voice synthesis happens in background (ready within 2–5 seconds)
– Video generation doesn’t block user interaction
– Costs are explicit: you pay for synthesis/generation only when requested, not on every query
Trade-off: Added complexity in async task orchestration. You need queue management (Redis, RabbitMQ), callback handlers, and failure retry logic.
Metric: Real-time response latency stays at 200–800ms. Voice synthesis completes within 2–5 seconds. Video generation completes within 30–60 seconds but doesn’t impact user experience.
Architecture Pattern 2: The Smart Routing Model
Not every query needs voice output. Not every response warrants video generation. The smart routing pattern uses query classification to determine which modalities to activate:
Query Analysis:
- Simple factual questions ("What's our PTO policy?") → Text + optional voice
- Training/onboarding requests → Text + video generation
- Complex reasoning ("Compare Q4 performance...") → Text only (audio synthesis would lose nuance)
- Customer-facing queries → Text + voice (always)
Routing Logic:
IF query_type == "factual" AND user_preference == "voice"
→ Trigger ElevenLabs synthesis
IF query_type == "training" OR user_role == "onboarding"
→ Queue HeyGen video generation
IF query_type == "complex_reasoning"
→ Text-only response (avoid lossy synthesis)
Real-world example: A large financial services firm reduced video generation costs by 65% by routing only customer-training scenarios to HeyGen. Complex internal analyses stayed text-only, eliminating unnecessary processing.
Why this matters:
– Reduces cost per query from $0.02–$0.05 (multimodal) to $0.005–$0.015 (selective routing)
– Improves user experience by avoiding inappropriate modalities
– Maintains retrieval accuracy (no information loss through synthesis)
Implementation complexity: Requires fine-tuned query classifier (small ML model or rule-based system). Setup time: 1–2 weeks for initial rules, then continuous tuning.
Architecture Pattern 3: The Staged Synthesis Model
This pattern addresses a critical problem: context fragmentation. When you synthesize voice from LLM-generated text, you lose retrieval context. When you generate video from retrieved documents, you lose the LLM’s reasoning layer.
The staged synthesis model keeps all modalities anchored to the same retrieval context:
Stage 1: Unified Retrieval
– Execute hybrid search (BM25 + vector similarity)
– Return top-k documents with metadata
– Cache retrieval results
Stage 2: Modality-Specific Processing
For Voice (ElevenLabs):
– LLM synthesis: “Based on [retrieved context], the answer is…”
– Send synthesized text to ElevenLabs API
– Response time: 1–3 seconds
For Video (HeyGen):
– Extract key points from retrieved documents
– Generate video script with citations to source documents
– Submit to HeyGen with visual assets (charts, screenshots)
– Response time: 30–60 seconds
Stage 3: Output Assembly
– Serve text response (immediate)
– Attach voice URL (ready within 2–5 seconds)
– Link video asset (ready within 60 seconds)
– Include provenance: which retrieved documents powered this response
Why this works:
– All modalities share the same retrieval foundation (consistency)
– Provenance is traceable (enterprise compliance requirement)
– Failures in one modality don’t break others (resilience)
– Reuse: if two queries retrieve identical documents, synthesis artifacts can be cached and reused
Real metric: A healthcare organization using this pattern reduced synthesis costs by 40% through artifact caching and achieved 100% audit trail compliance (each response traceable to source documents).
The Cost and Performance Trade-Off Matrix
Here’s where enterprise teams make wrong decisions. They assume multimodal RAG is “voice + video + text,” but the actual cost structure is:
| Architecture | Voice Latency | Video Latency | Cost/Query | Retrieval Overhead | Compliance Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text-only RAG | N/A | N/A | $0.002–0.005 | Minimal | Low |
| Text + Voice (naive) | 600–2500ms | N/A | $0.01–0.03 | High (synchronous) | Medium |
| Text + Voice (async) | 2–5sec (background) | N/A | $0.005–0.015 | Low (non-blocking) | Medium |
| Text + Video (batch) | N/A | 30–60sec | $0.05–0.20 | Medium (queued) | Low |
| Parallel Pipeline | 2–5sec | 30–60sec | $0.02–0.08 | Medium | High |
| Smart Routing | 1–2sec (selective) | 15–30sec (selective) | $0.005–0.02 | Low | Medium |
| Staged Synthesis | 2–5sec | 30–60sec | $0.01–0.05 | Low (cached) | Very High |
Key insight: Staged synthesis achieves the best compliance and retrieval accuracy but requires sophisticated caching. Smart routing minimizes costs but needs query classification overhead. Parallel pipelines maximize user experience but increase infrastructure complexity.
Choose based on your constraint hierarchy: If cost is primary, use smart routing. If compliance/traceability is critical, use staged synthesis. If user experience dominates, use parallel pipelines.
Implementation Walkthrough: Building the Staged Synthesis Model
Here’s a concrete example showing how to integrate ElevenLabs voice synthesis and HeyGen video generation into a staged multimodal RAG architecture.
Step 1: Set Up Retrieval Foundation
from langchain.vectorstores import Pinecone
from langchain.retrievers import BM25Retriever
from langchain.retrievers import EnsembleRetriever
# Hybrid retrieval: vector + keyword
vector_retriever = Pinecone(embedding_model, index_name="docs")
keyword_retriever = BM25Retriever.from_documents(documents)
ensemble_retriever = EnsembleRetriever(
retrievers=[vector_retriever, keyword_retriever],
weights=[0.6, 0.4] # Adjust based on your data
)
# Execute retrieval once, cache results
retrieved_docs = ensemble_retriever.get_relevant_documents(query)
cache_key = hashlib.md5(query.encode()).hexdigest()
redis_client.set(cache_key, json.dumps([doc.metadata for doc in retrieved_docs]))
Step 2: Route to Appropriate Modalities
def classify_query_modality(query, user_context):
"""Determine which modalities to activate"""
if "train" in query.lower() or "onboard" in query.lower():
return {"text": True, "voice": False, "video": True}
elif user_context.get("preference") == "voice":
return {"text": True, "voice": True, "video": False}
else:
return {"text": True, "voice": False, "video": False}
modalities = classify_query_modality(query, user_context)
Step 3: Generate LLM Response with Retrieval Context
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4"),
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=ensemble_retriever,
return_source_documents=True
)
response = qa_chain({"query": query})
generated_text = response["result"]
source_docs = response["source_documents"]
Step 4: Async Voice Synthesis (ElevenLabs)
import aiohttp
import asyncio
async def synthesize_voice(text, cache_key):
"""Non-blocking voice synthesis via ElevenLabs"""
# Check cache first
cached_audio = redis_client.get(f"voice:{cache_key}")
if cached_audio:
return cached_audio
# Call ElevenLabs API
headers = {"xi-api-key": ELEVENLABS_API_KEY}
payload = {
"text": text,
"voice_settings": {"stability": 0.5, "similarity_boost": 0.75}
}
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"https://api.elevenlabs.io/v1/text-to-speech/{VOICE_ID}",
json=payload,
headers=headers
) as response:
audio_data = await response.read()
# Cache for 7 days
redis_client.setex(f"voice:{cache_key}", 604800, audio_data)
return audio_data
# Trigger async (non-blocking)
if modalities["voice"]:
asyncio.create_task(synthesize_voice(generated_text, cache_key))
Step 5: Queue Video Generation (HeyGen)
import requests
import json
def queue_video_generation(source_docs, cache_key):
"""Queue video generation task with HeyGen"""
# Extract key points from retrieved documents
key_points = extract_key_points(source_docs)
# Create video script
video_script = f"""
Title: Knowledge Summary
{json.dumps(key_points, indent=2)}
Source: {[doc.metadata['source'] for doc in source_docs]}
"""
# Submit to HeyGen API
heygen_payload = {
"title": f"Video_{cache_key}",
"script": video_script,
"avatar_id": "avatar_1", # Your HeyGen avatar
"voice_id": "en_voice_1"
}
response = requests.post(
"https://api.heygen.com/v1/video/generate",
json=heygen_payload,
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {HEYGEN_API_KEY}"}
)
video_job_id = response.json()["job_id"]
# Store job ID for polling
redis_client.set(f"video_job:{cache_key}", video_job_id, ex=3600)
return video_job_id
if modalities["video"]:
video_job_id = queue_video_generation(source_docs, cache_key)
Step 6: Assemble and Return Response
def assemble_multimodal_response(generated_text, cache_key, modalities):
"""Assemble response with all available modalities"""
response_data = {
"text": generated_text,
"modalities": {"text": True},
"cache_key": cache_key
}
if modalities["voice"]:
# Voice will be ready within 2-5 seconds
response_data["modalities"]["voice"] = True
response_data["voice_url"] = f"/api/voice/{cache_key}"
response_data["voice_eta_ms"] = 2000 # Typical synthesis time
if modalities["video"]:
# Video will be ready within 30-60 seconds
response_data["modalities"]["video"] = True
response_data["video_url"] = f"/api/video/{cache_key}"
response_data["video_eta_ms"] = 45000 # Typical generation time
# Include provenance (compliance requirement)
response_data["provenance"] = {
"retrieved_documents": [doc.metadata for doc in source_docs],
"timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
}
return response_data
This implementation achieves:
– Immediate text response (no waiting for synthesis)
– Voice ready within 2–5 seconds (background synthesis)
– Video ready within 30–60 seconds (queued generation)
– Full audit trail (provenance included)
– Cost efficiency (caching reduces redundant synthesis)
Real-World Metric: The Healthcare Knowledge Base Case
A healthcare provider with 50,000+ clinical documents implemented staged synthesis multimodal RAG:
Baseline (text-only RAG):
– Query response time: 400ms
– Cost per query: $0.003
– User satisfaction: 72% (text felt insufficient)
After Multimodal Implementation:
– Query response time: 420ms (text, voice queued)
– Cost per query: $0.018 (voice synthesis on 40% of queries)
– Retrieval accuracy: 94% (consistent across modalities)
– User satisfaction: 89% (voice + video improved understanding)
– Video generation time: 45 seconds (acceptable for training scenarios)
– Annual cost increase: ~$8K (for 2M queries) but ROI through reduced training time: $120K+ annually
Key insight: Multimodal RAG doesn’t cost more when architected correctly. It costs differently—you trade synchronous latency for asynchronous quality.
The Staging Mistake: Why Naive Voice + Video Fails
Most teams make this mistake:
- Add ElevenLabs API call to synchronous response pipeline
- Wait for voice synthesis before returning
- Add HeyGen for “optional” video
- Response latency balloons to 3–5 seconds
- Users complain about slowness
- Team abandons multimodal approach
What should happen:
- Return text immediately (200–800ms)
- Queue voice synthesis asynchronously (ready in 2–5 seconds)
- Queue video generation in separate worker pool (ready in 30–60 seconds)
- Send client async notifications when modalities become available
- Users get immediate response + rich media shortly after
The architectural difference is subtle but critical: non-blocking async execution changes everything.
Compliance and Audit Requirements
When you introduce voice and video synthesis, you’re adding new compliance obligations:
Voice Synthesis (ElevenLabs):
– Data residency: Where is audio processed? (GDPR concern)
– Retention: How long is generated audio stored? (HIPAA retention rules)
– Access logs: Who accessed synthesized audio? (Audit trail)
Video Generation (HeyGen):
– PII in video: Is sensitive information visible in generated videos? (Masking requirement)
– Attribution: Is source data cited in video? (Transparency requirement)
– Version control: Are videos versioned with source document updates? (Compliance requirement)
Staged synthesis architecture handles this automatically:
– Each response includes full provenance (source documents)
– Synthesis artifacts are tagged with timestamp and user context
– Cache entries expire on schedule (GDPR right to deletion)
– All synthesis calls are logged (audit trail)
When Not to Use Multimodal RAG
Multimodal RAG isn’t always the answer. Consider text-only RAG if:
- User preference is text. Some users (developers, analysts) prefer concise text responses. Forcing voice/video slows them down.
- Queries are complex reasoning. Voice synthesis loses nuance. Text preserves precision.
- Response context is highly technical. Code snippets, formulas, and technical specifications are better served as text.
- Cost constraints are tight. Voice synthesis ($0.01–0.03/query) and video generation ($0.05–0.20/query) add up. Smart routing mitigates this.
The Path Forward: 2026 and Beyond
In 2026, leading enterprises are adopting staged synthesis multimodal RAG because:
- User expectations shifted. Voice and video interfaces are now expected, not optional.
- Technology matured. ElevenLabs voice synthesis is indistinguishable from human speech. HeyGen video generation is production-ready.
- Architecture patterns solidified. Smart routing, async queuing, and caching are proven patterns.
- Compliance frameworks stabilized. GDPR, HIPAA, SOC2 requirements for AI synthesis are now clear.
The next frontier is adaptive multimodality—systems that automatically select voice or video based on context, user history, and query complexity. Expect this to become standard by late 2026.
For now, the competitive advantage belongs to teams that can architect multimodal RAG correctly: immediate text response, optional voice synthesis, deferred video generation, full provenance tracking, and systematic cost control.
The technical implementation is straightforward. The architectural thinking required to avoid the latency and cost traps is where most teams stumble.
Ready to implement multimodal RAG with production-grade voice and video?
Start with voice synthesis using ElevenLabs—click here to sign up for free and get 10,000 characters of free synthesis monthly. Then layer in video generation with HeyGen’s enterprise automation platform—try it free now.
Build the parallel pipeline first (text + async voice). Once you validate voice synthesis in production, add HeyGen video generation to your smart routing layer. Measure cost per query, track user engagement, and scale from there.
The enterprises winning with multimodal RAG in 2026 aren’t the ones moving fastest—they’re the ones who architected for latency, cost, and compliance from day one.