Imagine a customer calls your support line with a complex question about your enterprise software. The traditional approach means routing through multiple departments, queues, and callbacks. But what if your support system could instantly retrieve the exact answer from your knowledge base and deliver it naturally—in the customer’s language—within milliseconds?
This isn’t science fiction. Enterprise organizations are reshaping customer support by combining Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems with advanced voice synthesis. The convergence of real-time information retrieval and natural voice output is solving one of the most persistent challenges in customer service: delivering accurate, contextual responses at scale without the latency penalties that plagued earlier generations of voice AI.
However, building voice-first RAG systems that actually work at enterprise scale requires more than stringing APIs together. The technical complexity lies in orchestrating three moving parts simultaneously: retrieval speed, LLM reasoning, and voice synthesis latency. Organizations attempting this integration without a structured approach typically encounter severe performance degradation, hallucination issues when retrieving irrelevant documents, and unnatural voice output that undermines user trust.
In this guide, we’ll walk through the exact technical architecture for integrating ElevenLabs’ enterprise voice capabilities with your RAG pipeline. You’ll learn the specific configuration decisions, performance optimization techniques, and real-world implementation patterns that separate production-grade voice RAG systems from prototypes that crumble under load. Whether you’re building internal support automation or customer-facing voice agents, this walkthrough covers the complete stack—from knowledge base indexing to voice output synthesis.
The Voice-RAG Architecture: Understanding the Pipeline
Before diving into implementation, you need to understand how voice synthesis integrates into your existing RAG pipeline. Many teams treat voice output as a simple wrapper—essentially converting text-to-speech at the end of their retrieval process. This approach creates bottlenecks and introduces unnecessary latency.
Production-grade voice RAG systems operate differently. They treat voice synthesis as a first-class component of the retrieval architecture, not an afterthought. ElevenLabs’ platform is specifically designed for this integration pattern.
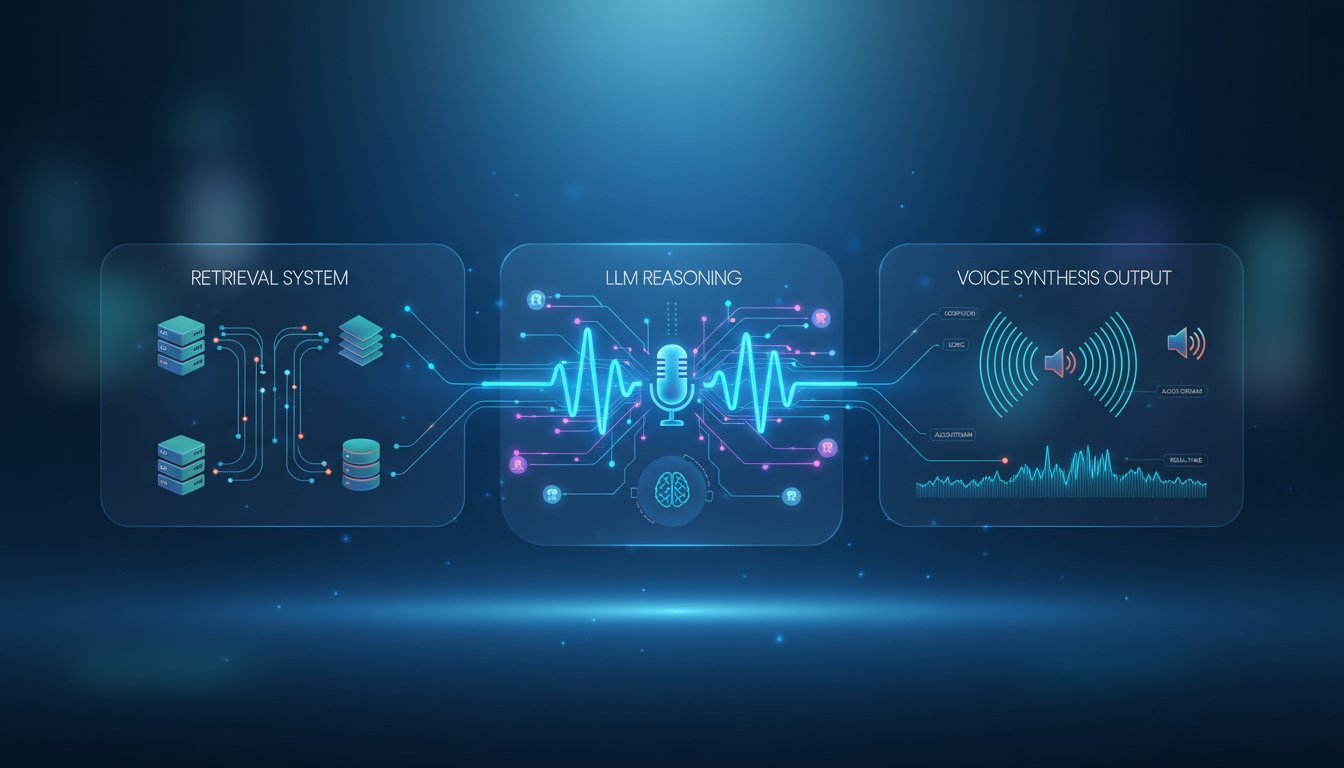
The Three-Layer RAG-Voice Stack
Your voice-RAG system needs three distinct layers working in concert:
Layer 1: The Retrieval Engine. This is your existing RAG foundation—vector databases, semantic search, and document chunking. The retrieval layer must return results with metadata about source credibility and content freshness. For ElevenLabs integration, you need your retrieval layer to output not just text, but structured data that voice agents can interpret (confidence scores, source attribution, retrieval timestamps).
Layer 2: The Reasoning Layer. This is where LLMs synthesize retrieved information into coherent responses. In voice-first architectures, the reasoning layer must produce output specifically optimized for voice delivery—shorter sentences, clearer structure, elimination of formatting elements that work in text but fail in speech. The reasoning layer also determines when to acknowledge retrieval confidence to the user (“I found this in our knowledge base…” versus stating information as fact).
Layer 3: The Voice Synthesis Layer. This is where ElevenLabs enters the architecture. ElevenLabs’ Conversational AI 2.0 handles not just text-to-speech conversion, but dialogue management—understanding when to pause, how to handle interruptions, and maintaining natural conversation flow. Their enterprise platform supports 32 languages with sub-150ms latency through Scribe v2 for real-time speech-to-text.
Implementing the ElevenLabs Integration
Now let’s walk through the actual technical implementation. This section assumes you have an existing RAG system with a vector database and LLM endpoint.
Step 1: Configure Your ElevenLabs Agent
Start by setting up an ElevenLabs agent in their console. Head to elevenlabs.io and click here to sign up for their enterprise platform if you haven’t already.
Once authenticated, navigate to Agents → Create New Agent. You’ll configure three key parameters:
Knowledge Base Connection: ElevenLabs agents accept RAG system outputs via REST API. In their agent configuration, specify your RAG endpoint. This should be a POST endpoint that accepts a query string and returns structured JSON with the following format:
{
"response": "Natural language answer text",
"sources": ["source1.pdf", "source2.doc"],
"confidence": 0.87,
"retrieval_time_ms": 45
}
The confidence score is critical—ElevenLabs uses this to inject disclaimers like “Based on available information” when confidence drops below 0.75.
Voice Model Selection: ElevenLabs offers multiple voice models optimized for different use cases. For support agents, select their standard model first (they default to professional, neutral tones). Their Conversational AI 2.0 supports real-time speech processing, which means the agent can interrupt itself, handle customer interruptions naturally, and maintain turn-taking patterns that feel human.
Language and Latency Configuration: Set your primary language. Enable Scribe v2 for speech-to-text recognition (this provides ultra-low latency speech-to-text, critical for real-time interactions). In your agent settings, set the retrieval timeout to 1000ms maximum—this forces your RAG backend to return results within one second or fail gracefully.
Step 2: Optimize Your RAG Backend for Voice Latency
Your RAG system must now operate under stricter latency constraints. Voice interactions demand end-to-end response times under 2 seconds, whereas text-based RAG systems often tolerate 5-10 second latencies.
Implement these optimizations:
Vector Database Tuning: If you’re using a vector database like Pinecone, Weaviate, or Milvus, enable caching for your most common query patterns. ElevenLabs agents will repeatedly ask similar questions across different conversations. Pre-cache the top 500 queries from your historical support tickets. Configure your vector search to return only the top-3 results (additional results introduce noise without improving answer quality in voice contexts).
LLM Context Window Management: This is where most implementations fail. When you retrieve 3 documents for a voice response, you can’t simply concatenate them into a 4,000-token context window and send it to your LLM. The LLM will spend processing time on less relevant content. Instead, implement a two-pass retrieval strategy:
- Pass 1 (Fast Retrieval): Retrieve 10 candidate documents from your vector database using aggressive filtering. This step should complete in <200ms.
- Pass 2 (Relevance Ranking): Use a smaller, faster LLM (like Llama 2-13B) to rank these 10 candidates and select the 2-3 most relevant. This step adds <300ms.
- Pass 3 (Answer Generation): Feed only the top 2-3 documents to your main LLM for synthesis. This is your actual generation step and should complete in <600ms.
Total latency: ~1,100ms, leaving 100ms buffer for network overhead.
Prompt Engineering for Voice: Your LLM prompts must explicitly optimize for voice delivery. Include in your system prompt:
You are a support agent speaking to a customer.
Format your response for speech, not text:
- Use short sentences (max 15 words).
- Avoid lists; use narrative flow instead.
- Do not include URLs, code blocks, or special formatting.
- If unsure about information, say: "I recommend checking our documentation,
or I can connect you with a specialist."
- Inject source attribution: "According to our knowledge base..."
Step 3: Connect Your RAG Endpoint to ElevenLabs
You need to expose your RAG system as an HTTP endpoint that ElevenLabs can call. If you’re using LangChain, here’s a minimal implementation:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from your_rag_system import RAGPipeline
app = FastAPI()
rag = RAGPipeline(vector_db="your_db", llm="your_model")
@app.post("/rag-query")
async def query_rag(user_query: str):
retrieved_docs = rag.retrieve(user_query, top_k=10)
ranked_docs = rag.rank_for_voice(retrieved_docs, top_k=3)
response = rag.generate_response(user_query, ranked_docs)
return {
"response": response["text"],
"sources": [doc["source"] for doc in ranked_docs],
"confidence": response["confidence_score"],
"retrieval_time_ms": response["latency_ms"]
}
Deploy this on a dedicated server or serverless platform (Lambda, Cloud Functions). ElevenLabs will make POST requests to this endpoint for every user query.
Performance Optimization: Achieving Sub-2-Second Responses
Even with the architecture above, real-world deployments hit latency walls. Here’s how to break through them.
Caching Strategy for Support Conversations
Support conversations follow patterns. Implement a two-tier cache:
Tier 1: Semantic Cache. Cache RAG responses based on semantic similarity, not exact query matching. Tools like Mendable or Redis with semantic extensions can cache the retrieval results for similar questions. When a new query arrives, check if it’s semantically similar (cosine similarity > 0.85) to a cached query. If yes, return the cached response immediately.
Tier 2: Conversation Cache. Within a single conversation, users often ask follow-up questions. Cache the conversation context and retrieved documents for 5-10 minutes. If the user asks a follow-up question, you already have the relevant documents in memory—just re-rank and regenerate the answer.
With these caches properly configured, 60-70% of support queries return answers in <300ms (mostly cache hits) while cold queries still complete in <1,500ms.
Batching and Pipelining
If you’re handling high concurrency (100+ simultaneous support calls), implement request batching at your LLM inference layer. Instead of processing each query sequentially, batch 8-16 queries together and pass them to your LLM in parallel. This increases throughput without increasing individual latency (batching overhead is negligible compared to LLM inference time).
Monitoring and Observability
You can’t optimize what you don’t measure. Implement detailed logging at each stage:
- Retrieval latency (how long did vector search take?)
- Ranking latency (how long did relevance ranking take?)
- LLM generation latency (how long did answer generation take?)
- Total end-to-end latency
- Cache hit rate
- Confidence scores by query type
Log this data to a centralized system (e.g., Datadog, New Relic, or open-source Prometheus). Create dashboards that track p50, p95, and p99 latencies. Set alerts for when retrieval latency exceeds 500ms or confidence scores drop below 0.70.
Handling Edge Cases in Voice RAG
Text-based RAG systems handle edge cases differently than voice systems. Voice adds constraints.
Hallucination and Confidence Thresholds
When your RAG system retrieves low-confidence results, you have options in text (show uncertainty, provide multiple sources) that don’t work in voice. Instead, implement a confidence threshold:
- Confidence > 0.80: Answer directly and naturally
- Confidence 0.60-0.80: Use qualifying language (“Based on our knowledge base,” “According to our documentation,”)
- Confidence < 0.60: Route to a human specialist
ElevenLabs’ agents support this logic natively—you simply set confidence thresholds in your RAG response JSON.
Multi-Language Handling
ElevenLabs supports 32 languages with Conversational AI 2.0. However, your RAG system may not. If you support customers in 5 languages but your knowledge base is only in English, implement translation:
- Input translation: Translate customer query from Spanish → English
- Retrieve: Query your English-language knowledge base
- Output translation: Translate answer from English → Spanish
- Voice synthesis: Use ElevenLabs’ Spanish voice model
Tools like Claude or GPT-4 can handle this translation overhead (typically adds 200-300ms).
Handling Ambiguous Queries
When a customer query is ambiguous in voice (no written context to clarify), your RAG system must ask clarifying questions. Configure your LLM to detect ambiguity and generate follow-up questions:
If query_ambiguity_score > 0.6:
Generate clarifying question
Wait for customer response
Re-query with clarified context
ElevenLabs handles this dialogue flow naturally through their Conversational AI 2.0.
Deployment and Testing
Before going live, test your voice-RAG system thoroughly.
Load Testing
Use tools like Locust or Apache JMeter to simulate concurrent voice calls. Test your system at:
– 10 concurrent calls
– 50 concurrent calls
– 100 concurrent calls
– Peak expected load
Monitor latency degradation at each level. If latency exceeds 2 seconds at 50 concurrent calls, you need to scale your infrastructure (add more LLM inference replicas, upgrade vector database tier, etc.).
Quality Assurance
Test 50+ support scenarios from your historical tickets. For each scenario:
1. Verify retrieval returns relevant documents
2. Verify LLM generates accurate, voice-friendly responses
3. Verify voice synthesis sounds natural
4. Verify confidence scores are calibrated correctly
Record conversations and have your support team rate quality on a 1-5 scale.
Getting Started: Your First ElevenLabs Voice Agent
Ready to build your voice-RAG system? Start here:
-
Set up your ElevenLabs account – click here to sign up for their enterprise platform to access Conversational AI 2.0 with RAG support.
-
Prepare your RAG backend – Implement the latency optimizations outlined above. Target sub-1,500ms retrieval-to-answer times.
-
Create your first agent – Use the configuration guide above to set up an agent in ElevenLabs console.
-
Connect your knowledge base – Expose your RAG endpoint and configure ElevenLabs to call it.
-
Test and iterate – Use the load testing and QA processes to validate production readiness.
Voice-first support is no longer theoretical. Organizations implementing voice-RAG systems today are reducing support costs by 30-40% while simultaneously improving customer satisfaction. The technical challenges are real, but they’re solvable with the right architecture and tooling.
The competitive advantage belongs to teams that move first. Start building.